If property you included in a GAA is later used in a personal activity, see Terminating GAA Treatment, later. For a short tax year of 4 or 8 full calendar months, determine quarters on the basis of whole months. The midpoint of each quarter is either the first day or the midpoint of a month.
Free Double Declining Balance Depreciation Template (Calculator)
Under this convention, you treat all property placed in service or disposed of during any quarter of the tax year as placed in service or disposed of at the midpoint of that quarter. This means that, for a 12-month tax year, 1½ months of depreciation is allowed for the quarter the property is placed in service or disposed of. The recovery period of property is the number of years over which you recover its cost or other basis. It is determined based on the depreciation system (GDS or ADS) used. The election must be made separately by each person owning qualified property (for example, by the partnerships, by the S corporation, or for each member of a consolidated group by the common parent of the group).
Declining Balance Method: What It Is and Depreciation Formula
Depreciation allowed is depreciation you actually deducted (from which you received a tax benefit). Depreciation allowable is depreciation you are entitled to deduct. If you depreciate your property under MACRS, you may also have to reduce your basis by certain deductions and credits with respect to the property.
Step 4: Compute the Final Year Depreciation Expense
The election must generally cover all property in the same property class that you placed in service during the year. However, the election for residential rental property and nonresidential real property can be made on a property-by-property basis. If you elect to claim the special depreciation allowance for any specified plant, the special depreciation allowance applies only for the tax year in which the plant is planted or grafted. The plant will not be treated as qualified property eligible for the special depreciation allowance in the subsequent tax year in which it is placed in service. For certain property with a long production period and certain aircraft placed in service after December 31, 2023, and before January 1, 2025, you can elect to take an 80% special depreciation allowance. You can elect to take a 100% special depreciation allowance for certain property with a long production period and certain aircraft placed in service before January 1, 2024.
- Sandra and Frank must adjust the property’s basis for the casualty loss, so they can no longer use the percentage tables.
- A measure of an individual’s investment in property for tax purposes.
- This method is the simplest to calculate, and generally represents the actual usage of assets over time.
- The nontaxable transfers covered by this rule include the following.
- Go to IRS.gov/SocialMedia to see the various social media tools the IRS uses to share the latest information on tax changes, scam alerts, initiatives, products, and services.

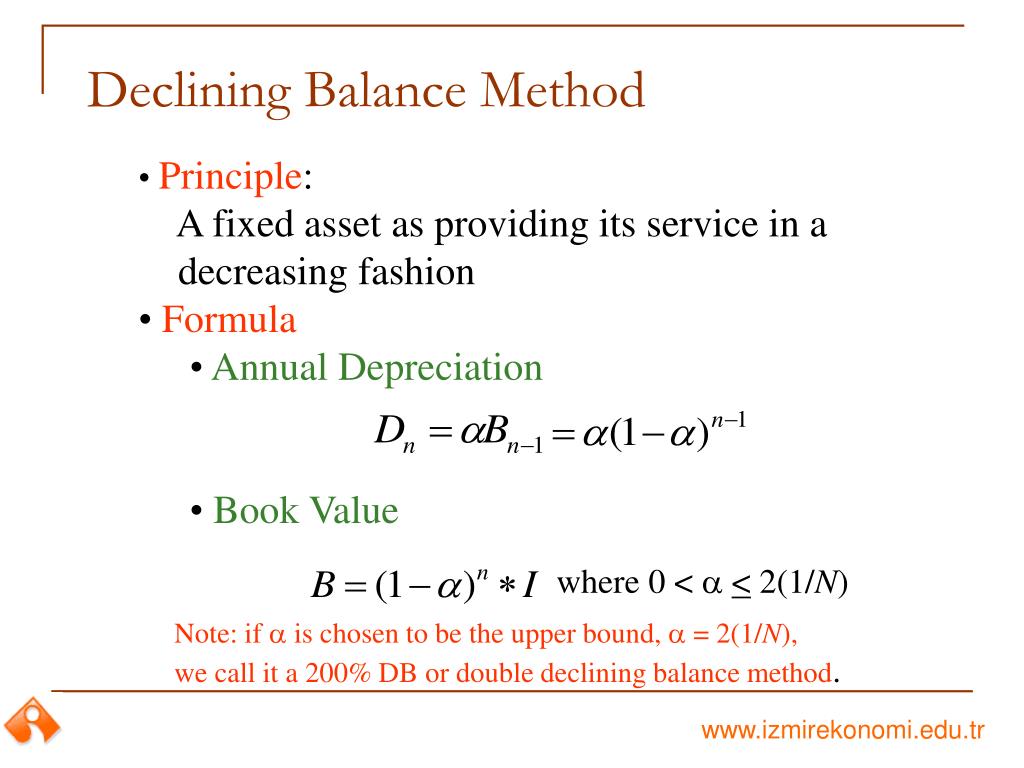
When using a declining balance method, you apply the same depreciation rate each year to the adjusted basis of your property. You must use the applicable convention for the first tax year and you must switch to the straight line method beginning in the first year for which it will give an equal or greater deduction. On October 26, 2022, Sandra and Frank Elm, calendar year taxpayers, bought and placed in service in their business a new item of 7-year property.
In the last year of an asset’s useful life, we make the asset’s net book value equal to its salvage or residual value. This is to ensure that we do not depreciate an asset below the amount we can recover by selling it. In 2016, the book value was $75,000, while in 2017, it fell to $60,000. Remember that the rate of depreciation remains constant but it is applied to a lesser amount (i.e., book value) each year.
In case of any confusion, you can refer to the step by step explanation of the process below. An exception to this rule is when an asset is disposed before its final year of its useful life, i.e. in one of its middle years. In that case, we will charge depreciation only for the time the asset was still in use (partial year). Like in the first year calculation, we will use a time factor for the number of months the asset was in use but multiply it by its carrying value at the start of the period instead of its cost. In the accounting period in which an asset is acquired, the depreciation expense calculation needs to account for the fact that the asset has been available only for a part of the period (partial year). When large amounts of depreciation are being recognized early in the life of an asset, this means that the carrying amount of the asset is severely reduced within a short period of time.
It is not confined to a name but can also be attached to a particular area where business is transacted, to a list of customers, or to other elements of value in business as a going concern. Travel between a personal home and work or job site within the area of an individual’s tax home. The Taxpayer Bill of Rights describes 10 basic rights that all taxpayers have when dealing with the IRS. Go to TaxpayerAdvocate.IRS.gov to help you understand what these rights mean to you and how they apply. TAS is an independent organization within the IRS that helps taxpayers and protects taxpayer rights. TAS strives to ensure that every taxpayer is treated fairly and that you know and understand your rights under the Taxpayer Bill of Rights.
Unlike the straight-line method, the double-declining method depreciates a higher portion of the asset’s cost in the early years and reduces the amount of expense charged in later years. Similar things xero accountants in auckland occur if the salvage value assumption is changed, instead. Suppose that the company changes salvage value from $10,000 to $17,000 after three years, but keeps the original 10-year lifetime.
Leave a Reply